Exploring Microservices Architecture with with Spring Cloud: Eureka and API Gateway
02-06-2023 - Shai Zambrovski
In today's rapidly evolving world of software development, building scalable and resilient applications has become a necessity.
Microservices architecture offers a solution by decomposing applications into smaller, independent services that can be developed, deployed, and scaled individually.
Two key components in the microservices landscape are Service Registry\Discovery and API Gateway.
Spring Cloud
Spring Cloud is a framework within the Spring ecosystem that provides a set of tools and libraries to simplify the development of distributed systems and microservices-based applications.
It aims to address common challenges in distributed computing, such as service discovery, configuration management, load balancing, and more.
Spring Cloud leverages popular technologies like Netflix OSS components (e.g., Eureka, Ribbon, Hystrix) and integrates them with Spring Boot to enable developers to easily build scalable, resilient, and cloud-native applications.
It promotes the use of microservices architecture and provides a consistent and opinionated approach to building distributed systems using Spring's programming model.
Api Gateway
An API gateway is a server or service that acts as an entry point for all client requests to a microservices architecture.
It provides a centralized point of control and management for APIs, allowing for features like authentication, rate limiting, request/response transformation, and routing to multiple services.
The API gateway acts as a single interface for clients, abstracting away the complexities of the underlying microservices and providing a unified and consistent API for clients to interact with.
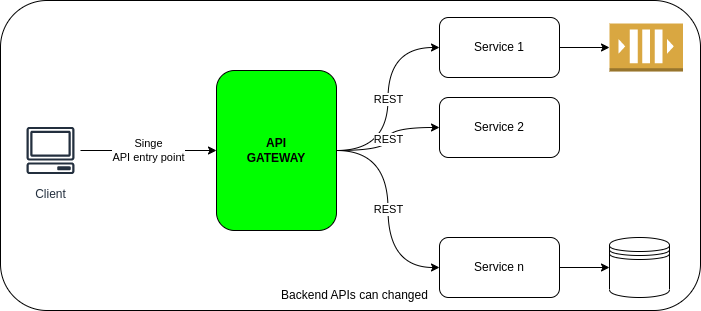
Spring Cloud API Gateway
Spring Cloud Gateway is a lightweight and highly customizable API gateway built on top of Spring Boot.
It provides a way to route and filter HTTP requests to backend services based on various criteria.
The gateway acts as a single entry point for all client requests, enabling centralized control and management of API traffic.
It supports dynamic routing, load balancing, and other advanced features to ensure reliability, scalability, and security of the microservices architecture.
Spring Cloud Gateway integrates seamlessly with other components of the Spring Cloud ecosystem, such as service discovery and configuration management, making it an ideal choice for building robust and resilient API gateways in distributed systems.
Service Registry\Discovery
In a distributed system composed of numerous services, the ability to locate and communicate with these services is vital. Service registry and discovery play a crucial role in managing the dynamic nature of these distributed architectures.
A service registry is a central repository where services can register their location and metadata, allowing other services to discover and interact with them. It serves as a directory or catalog of available services within the system.
Service discovery, on the other hand, is the mechanism through which services can locate and connect to other services dynamically. By leveraging the service registry, services can query and retrieve the necessary information to establish communication with their dependencies.
Service registry and discovery provide scalability, fault tolerance, and flexibility in distributed systems by enabling seamless service-to-service communication without hard-coded dependencies. They facilitate dynamic updates and scaling of services, making it easier to add, remove, or replace services in the system.
Client vs server side service discovery
Client service registry refers to the capability of a service or application to dynamically register itself with a service registry and provide its availability and metadata information for other services to discover and interact with.
Server service registry refers to the centralized repository or server that maintains the registry of available services, allowing other services to discover and communicate with them dynamically through a load balancer that has a well-known location.
| Client-Side Service Discovery | Server-Side Service Discovery |
|---|---|
| Pros Client services have control over service discovery and can make dynamic routing decisions. Less dependence on external components or infrastructure. Client services can easily adapt to changes in service availability. |
Cons Centralized service registry provides a single source of truth for service information. Improved scalability and performance by offloading service discovery to dedicated components. Easy integration with other infrastructure components like load balancers or API gateways. |
| Cons Increased complexity in client services due to the need for service discovery logic. Potential network overhead from querying the service registry for service information. Requires additional effort for handling service registry failures or inconsistencies. |
Cons Dependency on the availability and reliability of the central service registry. Possible performance impact due to the additional network hops to the service registry. May introduce a single point of failure if the service registry becomes unavailable. |
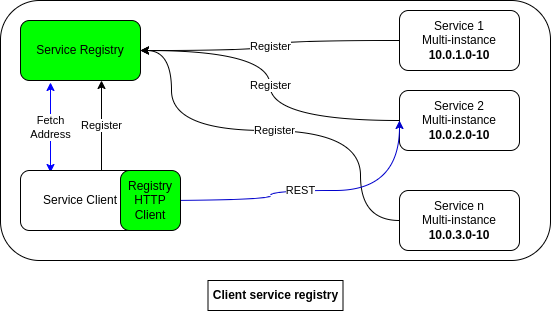 |
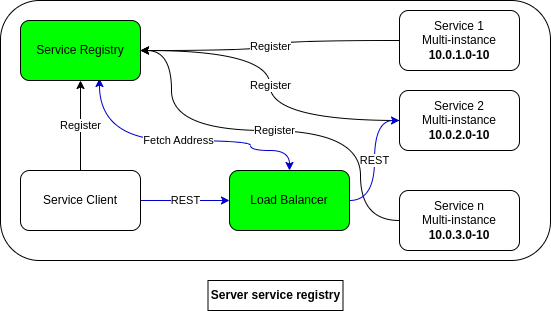 |
Spring Cloud Eureka
Spring Cloud Eureka is a service registry and discovery server that is part of the Spring Cloud framework. It is inspired by Netflix Eureka, which is an open-source project developed by Netflix as part of their Netflix OSS (Open Source Software) platform.
Spring Cloud Eureka implements client-side service discovery by providing a built-in client library that applications can use to register themselves with the Eureka server.
In this approach, each service instance (client) is responsible for registering itself with the Eureka server upon startup. The client sends heartbeats to the server to keep its registration information up to date.
Other services (clients) that need to consume a particular service can use the Eureka client library to discover the available instances of that service. The Eureka client library provides a simple API to query the Eureka server for service instances based on their registered service ID.
Demo

We will introducing the power of Spring Cloud API Gateway and Eureka using simple e-commerce web application built on-top of Docker Compose.
Our application is built with a microservices architecture
Spring Cloud Eureka server: Provides a service registry and discovery mechanism for seamless communication between microservices.
This is the pom.xml file for the Eureka server.
We use dependency management of spring-cloud and use only the eureka-server package to acts as a service registry.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.8-SNAPSHOT</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>io.shaikezam</groupId>
<artifactId>service-discovery</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>service-discovery</name>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2022.0.3</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-server</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<finalName>service-discovery</finalName>
</build>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<releases>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</releases>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>netflix-candidates</id>
<name>Netflix Candidates</name>
<url>https://artifactory-oss.prod.netflix.net/artifactory/maven-oss-candidates</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<releases>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</releases>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
</project>The provided YAML file configures the server port, eureka client host and application name:
spring:
application:
name: service-discovery
server:
port: 8001
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://service-discovery:8001/eureka
We will set in our main function the@EnableEurekaServer Spring annotation that enable the service to act as a Eureka server, allowing it to register other services and provide service discovery capabilities within a distributed system.
package io.shaikezam.servicediscovery;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.netflix.eureka.server.EnableEurekaServer;
@EnableEurekaServer
@SpringBootApplication
public class ServiceDiscoveryApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(ServiceDiscoveryApplication.class, args);
}
}Spring Cloud API Gateway: Serves as a centralized entry point, enabling advanced routing, filtering, and rate limiting for improved security and performance and serve our static resources.
This is the pom.xml file the APi Gateway.
We use dependency management of spring-cloud and use only the spring-cloud-starter-gateway package to acts as a api-gateway and the spring-cloud-eureka-client to register and discover other services.
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<project xmlns="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance"
xsi:schemaLocation="http://maven.apache.org/POM/4.0.0 https://maven.apache.org/xsd/maven-4.0.0.xsd">
<modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion>
<parent>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId>
<version>3.0.8-SNAPSHOT</version>
<relativePath/>
</parent>
<groupId>io.shaikezam.</groupId>
<artifactId>application</artifactId>
<version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version>
<name>application</name>
<properties>
<java.version>17</java.version>
<spring-cloud.version>2022.0.2</spring-cloud.version>
</properties>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-netflix-eureka-client</artifactId>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-starter-gateway</artifactId>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
<dependencyManagement>
<dependencies>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.springframework.cloud</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-cloud-dependencies</artifactId>
<version>${spring-cloud.version}</version>
<type>pom</type>
<scope>import</scope>
</dependency>
</dependencies>
</dependencyManagement>
<build>
<plugins>
<plugin>
<groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId>
<artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId>
</plugin>
</plugins>
<finalName>task-tracker-api-gateway</finalName>
</build>
<repositories>
<repository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<releases>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</releases>
</repository>
<repository>
<id>netflix-candidates</id>
<name>Netflix Candidates</name>
<url>https://artifactory-oss.prod.netflix.net/artifactory/maven-oss-candidates</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</repository>
</repositories>
<pluginRepositories>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-milestones</id>
<name>Spring Milestones</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/milestone</url>
<snapshots>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</snapshots>
</pluginRepository>
<pluginRepository>
<id>spring-snapshots</id>
<name>Spring Snapshots</name>
<url>https://repo.spring.io/snapshot</url>
<releases>
<enabled>false</enabled>
</releases>
</pluginRepository>
</pluginRepositories>
</project>The provided YAML file configures the server port, eureka server host and application name.
server:
port: 8000
spring:
application:
name: api-gateway
eureka:
client:
service-url:
defaultZone: http://service-discovery:8001/eureka
This Application class sets up a Spring Boot application with service discovery capabilities and configures routes for the Spring Cloud Gateway to forward requests to backend services based on defined path patterns:
@EnableDiscoveryClient annotation enables the service to participate as a discovery client, allowing it to register with a service registry and discover other services.
The customRouteLocator method is a bean definition that configures the routes for the Spring Cloud Gateway. It uses the RouteLocatorBuilder to define routes based on incoming paths and rewrite them to backend service URLs using load-balanced (lb) URIs.
The example shows two routes: "product-service" and "order-service", where the incoming paths "/webapi/products/" and "/webapi/orders/" are rewritten to "/api/v1/<API SUFFIX>" and forwarded to the respective backend services.
For example /webapi/products/foowill redirect to /api/v1/products/foo of product-service
package io.shaikezam.application;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.cloud.client.discovery.EnableDiscoveryClient;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.RouteLocator;
import org.springframework.cloud.gateway.route.builder.RouteLocatorBuilder;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
@EnableDiscoveryClient
@SpringBootApplication
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SpringApplication.run(Application.class, args);
}
@Bean
public RouteLocator customRouteLocator(RouteLocatorBuilder builder) {
return builder.routes()
.route("product-service", r -> r.path("/webapi/products/**")
.filters(f->f.rewritePath("/webapi/(?<segment>.*)","/api/v1/${segment}"))
.uri("lb://product-service"))
.route("order-service", r -> r.path("/webapi/orders/**")
.filters(f->f.rewritePath("/webapi/(?<segment>.*)","/api/v1/${segment}"))
.uri("lb://order-service"))
.build();
}
}Products Service: Handles operations related to products, such as retrieval, creation, and management.
Orders Service: Manages order-related functionalities, including order placement, processing, and tracking.
Both product-service and order-service are Spring boot application that written with MVC pattern that expose API in the controller, a service layer for BL and repository that implemented by Spring JdbcTemplate
Also, each service has it's own applicatiom.yml file that contains the service port, application name and eureka server host.
Also, each service has it's own applicatiom.yml file that contains the service port, application name and eureka server host.
MariaDB Service: Ensures persistent data storage for the application, maintaining the integrity and reliability of the data.
phpMyAdmin Service: Offers a user-friendly interface to manage and monitor the application's MariaDB database for easy debugging and data inspection.
This is the docker-compsoe.yml file (we open the ports for all service for debug purpose).
Feel free to change password (I choose to use Admin@Admin for DB & phpMyAdmin).
version: "3.9"
services:
api-gateway:
container_name: api-gateway
build: api-gateway
ports:
- "8000:8000"
networks:
- product-network
service-discovery:
container_name: service-discovery
build: service-discovery
ports:
- "8001:8001"
networks:
- product-network
product-service:
container_name: product-service
build: product-service
ports:
- "8002:8002"
networks:
- product-network
depends_on:
- db
order-service:
container_name: order-service
build: order-service
ports:
- "8003:8003"
depends_on:
- db
networks:
- product-network
db:
container_name: db
build: db
restart: always
environment:
MARIADB_ROOT_PASSWORD: admin
MARIADB_USER: admin
MARIADB_PASSWORD: admin
MARIADB_DATABASE: application
ports:
- "3306:3306"
networks:
- product-network
phpmyadmin:
image: phpmyadmin/phpmyadmin
container_name: phpmyadmin
restart: always
ports:
- "8004:80"
environment:
PMA_HOST: db
PMA_PORT: 3306
MARIADB_ROOT_PASSWORD: admin
networks:
- product-network
networks:
product-network:
external: false
name: product-networkThe above demo can be run after you clone my repository, just execute build.sh file and navigate to localhost:8000/index.htm
You can also navigate to eureka dashboard via localhost:8001.
